Chapter 22. Heredity
Page193
1. One possible choice is T for the dominant gene (allele) and t for the recessesive gene.
2. The chromosomes are in pairs (one from the male parent and one from the female parent) and
so the genes they carry must be in pairs. If both genes are dominant or both recessive, they
will control the characteristic in the same way. If one is recessive and one dominant they will
not affect the characteristic in the same way.
3. Since the gene for black hair is dominant over the gene for red hair, the person would have
black hair.
4. a For example: Gene for red hair b, gene for black hair B.
Combination for red hair - bb.
b You would expect a red-haired couple to breed true because they must both be bb.
c A black-haired couple could have a red-haired baby if they were both Bb.
5. Aa is heterozygous, AA is homozygous dominant, aa is homozygous recessive.
6. The gene for red, e.g. R is dominant over the gene for white r.
Page195
1. All the offspring must inherit one gene from the male parent and one from the female parent
so all the offspring must be Bb.
2. Only the BB mice will be true-breeding, i.e. one in three.
3. If white babies turn up in the second generation it means that one of the original parents must have been heterozygous Bb. (If both original parents were heterozygous you would expect some white offspring in the first generation).
The probable genotypes of this first generation will be BB Bb BB Bb (all black, but 50%
homozygotes and 50% heterozygotes).
If the BB black guinea pigs are mated with bb white guinea pigs all their offspring will be Bb black guinea pigs.
If the Bb black guinea pigs are mated with bb white guinea pigs you would expect half of their offspring to be Bb guinea pigs. Adding these results together gives one half black and the other half with equal numbers of black and white offspring.
Page 196
1. (left hand column) You would carry out a recessive test-cross. Each parent would be mated with a homozygous white rabbit. With the homozygous parent this would produce all black offspring but with the heterozygous parent there would be, on average, 50% black heterozygous and 50% white homozygous babies.
1. (right hand column) If both parents are homozygous AA x BB, the children will be Group AB.
If the mother was heterozygous (AO) the children could be AB or B A (AB or BO). If the father was heterozygous (BO) the children could be AB or A (AB or AO).
If both parents were heterozygous (AO, BO) the offspring could include groups A (AO) ,
B (BO), AB or O.
2. The man cannot be the father. The genes for groups A and B are dominant to O. So whether the woman is homozygous or heterozygous for the A gene, the offspring would have received a dominant A or B gene.
If the father was heterozygous for the B gene (BO) and the woman was heterozygous for the A gene (AO) the child could have inherited two O genes
3. a The alleles for red and white hairs are codominant
b
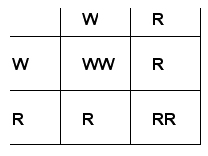 |
On average, there would be a ratio of one red (RR), one white (WW) and two roan (RW) in a succession of calves |
Page 197
1. The process of meiosis rules out the possibility of X sperms only. There will be an equal number of X and Y sperms in the father’s semen. There is a 50:50 chance of an XY or XX zygote. But this is indeed a matter of chance, and the sequence of 4 girls is due to chance alone.
Page 199
1. The genotype for a woman with sickle-cell trait would be HBaHbs. If she
a marries a normal man, whose genome would be HbaHba, none of the children would have
the disease but half of them could inherit the trait.
b marries a man with sickle cell trait, there is a 1in 4 chance that a child would be normal,
a 1 in 4 chance that a child will have the disease and a 1 in 2 chance that the child will have
the trait.
c marries a man with sickle cell disease (HbsHbs) two children in 4 could inherit the disease
and 2 children in 4 could inherit the trait.
|
Downloads
Download the answers in PDF format below
Section 1, Chapters 1-5
Section 2, Chapters 6-9
Section 3, Chapters 10-12
Section 3, Chapters 13-17
Section 3, Chapters 18-20
Section 4, Chapters 21-24
Section 5, Chapters 25-27
Section 5, Chapters 28-29
Section 6, Chapters 30-34
Section 6, Chapters 35-37
Section 7, Chapters 38-39
Section 8, Chapters 40-41
|

